Patanjali’s Yoga Sutras – Chapter 1: (Un-coloring Your Thoughts; Sutra 1.5)
Part 1 (*link below) in this series ended with the forth Yoga Sutra (1.4) – vritti sarupyam itaratra, which says: “At other times, when one is not in self-realization, the Seer appears to take on the form of the modifications of the mind field, thereby taking on the identity of those thought patterns.”
Those gross and subtle thought patterns (vrittis) referred to in (1.4) fall into five types, that block the realization of the true Self, of which some are colored (klishta) and
others are uncolored (aklishta). The five varieties of thought patterns to witness are: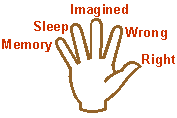
- 1. Knowing correctly (pramana)
- 2. Incorrect knowing (viparyaya)
- 3. Fantasy or imagination (vikalpa)
- 4. The void-ness that is deep sleep (nidra)
- 5. Recollection or memory (smriti)
The Yogi learns to witness these five kinds of interfering thoughts with non-attachment, discriminating between these five, and to cultivating the first type of thought, which is knowing correctly, and there are three ways of gaining correct knowledge (pramana):
1. Perception
2. Inference
3. Testimony or verbal communication from others who have knowledge.
Incorrect knowledge (viparyaya) or fantasy or imagination (vikalpa) are both made up of thought patterns that may have verbal expression and knowledge, but for which there is no real object or basis in existence. Dreamless sleep (nidra) is the subtle thought pattern which has absence or non-existance as its object. Recollection or memory (smriti) is mental modification of a previous impression.
Now on to the sutras…
Yoga Sutra (1.5) – vrittayah pancatayah klishta aklishta. Vrittayah means “the vrittis are;” pancatayah means fivefold (and designates two kinds), panch means five; klishta comes from the root klish (to cause trouble colored, painful, afflicted, impure); aklishta, the root “a” means without or in the absence of, therefore is the opposite of klishta, being uncolored, not painful, not afflicted, pure or absent of the coloring called klishta.
So the sutra basically says; “Those gross and subtle thought patterns (vrittis) fall into five types or varieties, some of which are colored (klishta) and others that are uncolored (aklishta).” Those that are colored (klishta) have to do with ignorance, ego-self, attachments, aversions, and fears. The simple witnessing of whether thought patterns are colored or not colored is an extremely useful part of the process of purifying, balancing, stabilizing and calming the mind so that meditation can deepen.
, and we may come to experience our true “Self” (Atman). The joys of deeper meditation come through uncoloring these mental obstacles (hindrances) that veil the true Self. This uncoloring process is an extremely important concept, and is further dealt with in chapter 2 of Patanjali’s Yoga Sutras. It is such an important concept that it is virtually impossible to properly practice Yoga without understanding it.
Thoughts that are colored (klishta) move away from enlightenment and result in bondage, whereas uncolored thoughts (akleshta) move towards enlightenment, resulting in freedom.
Further commentary on this sutra (1.5):
To observe the coloring of our thought patterns is one of the most useful practices of Yoga, and can be done throughout the day. This meditation in action, or mindfulness, can be of tremendous value in clearing the clouded mind, so that during your seated meditation time, that practice can go much deeper.
Witnessing the coloring of thoughts means that whenever a thought and its accompanying emotion arises, you simply identify it as, “This is colored,” or “This is not colored.” Similarly, when confronted with whether some decision or action is useful or not also brings great control over your of minds habits. Again, it is witnessing, and distinguishing between, “This is useful,” or “This is not useful.”
Stay tuned, this series will continue with: Part 3 (Un-coloring Your Thoughts, cont.) beginning with Yoga Sutra (1.6)
*Part 1 can be viewed by clicking on: The Teachings of Yoga (Part 1 – Yoga Defined)
Of related interest, click on: The Problem of Thoughts & Yoga’s Solution
*Rae Indigo is ERYT500.
